Symptoms of Brain Cancer
There are many different signs and symptoms associated with brain cancer. They will vary to some degree based on the type of brain tissue that is being affected by the cancer. For example, a patient who has a cancer in the Occipital lobe of the brain will have generalized symptoms as well as symptoms that are focal to the Occipital area of the brain such as vision change. For those patients with a brain tumor invading the Temporal area of the brain, they will experience symptoms such as speech impairment.
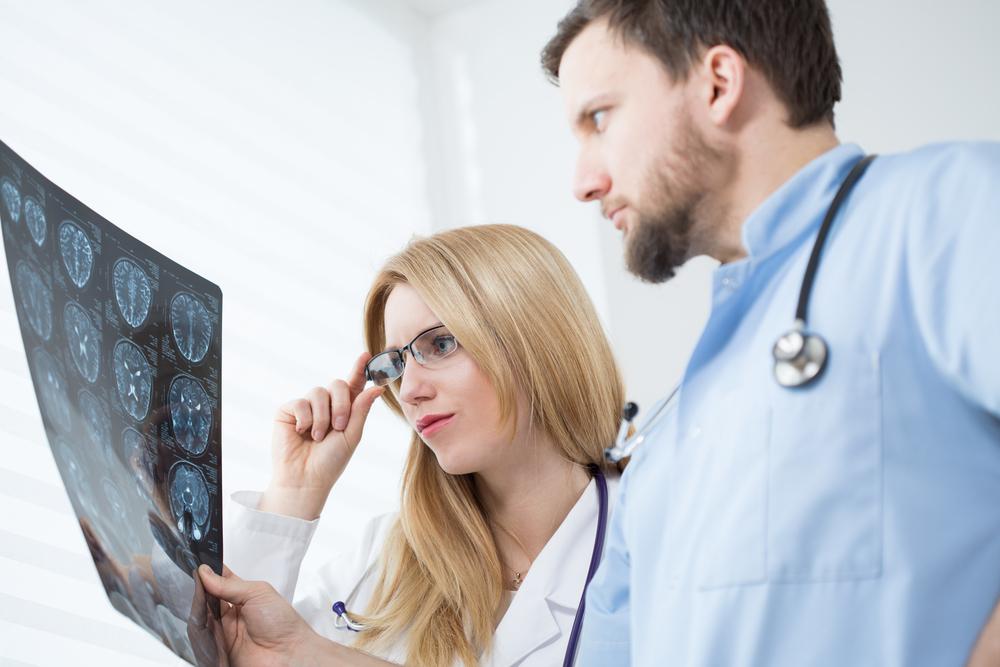

There are generalised symptoms that should be considered red flags and warrant further evaluation to provide more conclusive results.
Symptoms and signs to be aware of include:
- New onset of headaches.
- If you normally get headaches, try to notice if there is a difference in the pattern associated with your headaches. Headaches may become more frequent in number as well as more severe.
- If you have unexplained headaches, or new onset headaches, it is imperative that you see a physician so that further evaluation can rule out any serious medical conditions that may be life-threatening.
- Nausea and vomiting that cannot be explained through other medical conditions (i.e. pregnancy, virus, gastroenteritis, etc).
- Patients with brain tumours will often first notice vision changes, which may include the following: blurred vision, double vision, loss of peripheral vision or other vision problems.
- Depending on the area of the brain involved, patient’s symptoms may include: loss of motor of sensory in the upper or lower extremities. This means that the patients may start to experience the inability to move their arms or legs; these patients may also notice changes in sensation as well.
- Brain tumours may also cause loss of balance, or difficulty maintaining balance; speech difficulties; and confusion with regards to their daily tasks that they have had no difficulty completing in the past.
- Confusion setting in, without warning.
- Hearing difficulties, or hearing loss may also be associated with certain brain tumours. Many patients may experience changes in their personality or behaviour. It is imperative to speak with friends and family who are around these individuals to determine if there has been any change in the patient’s behaviour or personality.
- Seizures are one of the most common presenting symptoms associated with brain tumours, especially in seizure-naive patients. If a patient presents to the emergency room after a seizure, and he/she does not have a history of seizures, it is imperative to rule out brain tumour.
These are just some of the generalised signs and symptoms associated with brain tumours. The symptoms will vary based on the type of tumour, size of the tumour, location of the tumour and degree of invasion of the tumour. Each individual is different, and an individualised evaluation and treatment plan should be established so that the patient will receive unique and specialised care for the best possible medical outcomes.