Major causes, symptoms, and risks of hearing loss
When you age, you can experience hearing loss, and that’s fairly common among people. In our country, approximately one-third of the population between the age group of 65 to 75 years have some or the other form of hearing loss. Moreover, every one in two persons over the age of 75 has this defect.
Types of hearing loss
- One that involves the inner ear – Sensorineural
- One that involves the middle or outer ear – Conductive
- Combination of the two – Mixed
Usually, hearing loss occurs because of prolonged exposure to loud noises or simply as a result of aging.
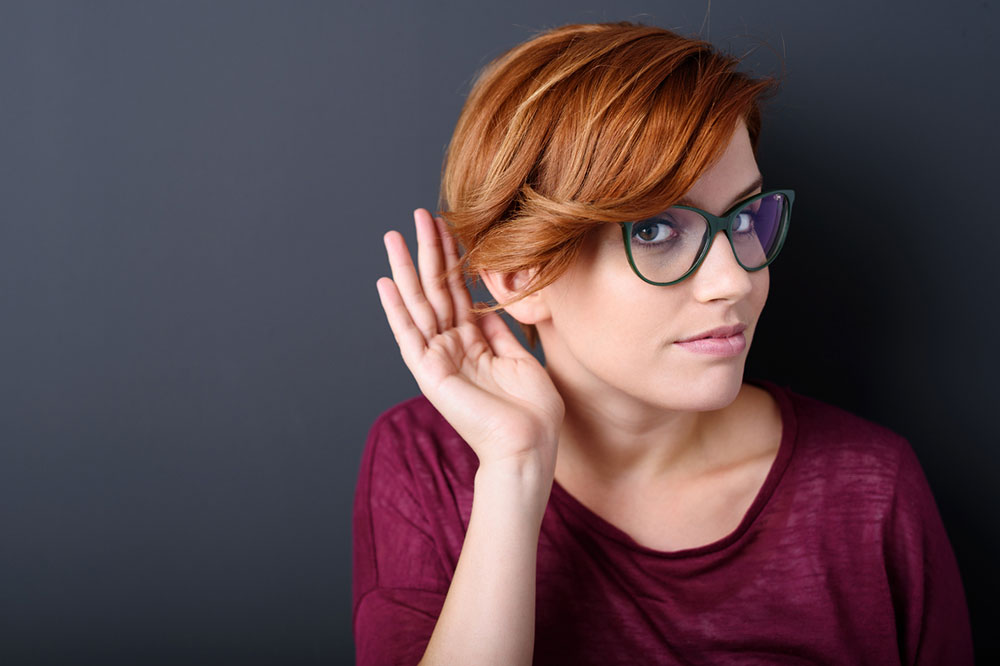

However, with the excessive accumulation of earwax, your hearing might be temporarily reduced. Though hearing loss cannot be reversed, certain steps can be taken to reduce its impact.
Symptoms of hearing loss
- Inability to comprehend words, especially in a crowded or a noisy place
- Repeatedly requesting people to speak loudly, clearly, and slowly
- Trying to withdraw from conversations
- Muffling of sounds
- Inability to hear consonants
- Having to keep the radio or the television sound up
Causes
- Build-up of earwax over time
When there’s a gradual build-up of earwax, it tends to obstruct the ear canal. As a result of it, the sound wave conduction gets hampered. Getting rid of earwax can help you get rid of hearing loss. - Tumor, ear infection, or abnormal growth
Either of these in the ear can lead to hearing loss. - Problem with inner ear
Prolonged exposure to loud noise or aging can also contribute to hearing loss. It is the nerve cells present in the cochlea, which sends the hearing signals to the brain. As and when these nerve cells are damaged, the efficient transmission of sound messages are restricted, and this leads to hearing loss. - Eardrum rupture
In case of a sudden burst of loud noise, eardrum poking by an object, an ear infection, or change in the pressure, there might be a rupturing of the eardrum, which can lead to hearing loss.
Risk factors
- Aging
With age, hearing loss becomes common. - Certain illnesses
A few illnesses or diseases, which result in meningitis or high fever can damage the cochlea and cause hearing loss. - Medications
There are a few medications, such as chemotherapy prescriptions, sildenafil, or gentamicin, which have a deteriorating effect on the inner ear. It might lead to hearing loss or cause tinnitus. In some cases, the effect is only temporary. Consuming a high dosage of certain medications like pain relievers and aspirin, among others can also lead to hearing loss. - Heredity
Your genes might also make you more vulnerable to ear damage or hearing loss from aging. - Loud noise
With prolonged exposure to loud noise or a short blast of a screechy sound (like that of a bullet), your inner ear can be damaged. It will lead to hearing loss. - Recreational noises
Exposure to sounds of jet engines or firearms can lead to permanent ear damage. In addition to this, a few other recreational sounds, such as listening to music at a loud volume, motorcycling, snowmobiling, or carpentry, can also have a similar impact. - Occupational noises
Jobs, such as construction works, farming, or factory work, where loud noise is a part of the routine, can also lead to a hearing loss.
Disclaimer:
The content of the articles discussing symptoms, treatments, health conditions, and side effects is solely intended for informational purposes. It is imperative that readers do not interpret the information provided on the website as professional advice. Readers are requested to use their discretion and refrain from treating the suggestions or opinions provided by the writers and editors as medical advice. It is important to seek the help of licensed and expert healthcare professionals when necessary.