Important Things You Need to Know about Diarrhea
Diarrhea should be diagnosed and treated beforehand to stop it from becoming a life-threatening disease. The common indications include a mild and temporary stomach upset or dehydration or severe bleeding in intestines causing excruciating abdominal pain. Among the people suffering from Diarrhea in the country, almost 90% are kids.
Mostly caused by virus, bacteria, and parasites, the symptoms of Diarrhea can be confusing as frequent defecation or loose stools are common in some people, especially the breastfeeding mothers.
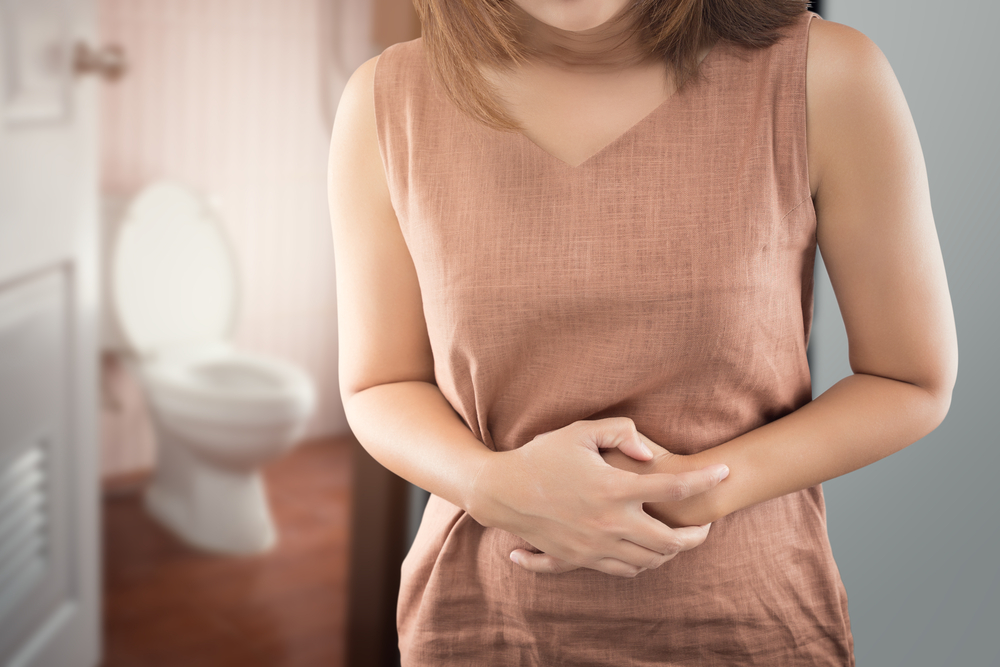

What are the causes of diarrhea?
For Traveler’s Diarrhea the contamination of food and water as well as lack of sanitization is among the main factors. Some of the common causes include contamination of viruses like rotavirus and norovirus, bacteria and parasites. Some antibiotics, antacids, cancer drugs can cause diarrhea, so does malfunction of colons and food intolerances (fructose, lactose, artificial sweeteners etc). If the patient has gone through surgery of the intestine or any part of the digestive system, mal-absorption or constipation can lead to Diarrhea. Excessive alcohol intake, radiation therapy especially for cancers and certain health issues like hyperthyroidism and Diabetes Mellitus are also responsible for causing diarrhea.
What are the symptoms of diarrhea?
Unusual abdominal pain, urgent need of defecation, loose motion, dehydration for more than two days, high fever and stools either tarry and black or bloody with pus are the most general symptoms of diarrhea. The common symptoms are as follows:
- Stomach or abdominal pain
- An unusual feeling of thirst
- Low urination, urine dark colored
- Bloating of the abdomen
- High fever, sometimes accompanied by chills
- Loss of weight
- Continuous vomiting and dehydration
- Mal-absorption and dehydration often lead to chronic diarrhea
- Nausea, drowsiness, confusion, irritability and increased heart rate, mostly seen in adults
As often general dehydration or stomach upset have quite the same symptoms, hence, under a certain period of time, medical attention becomes mandatory. If a kid has a black or bloody stool with mucus, over 102 degrees Fahrenheit temperature and dehydration occurring continuously for more than 24 hours, consulting a doctor becomes necessary.
As for adults, if dehydration, severe rectal or abdominal pain, blackish or bloody stools and over 102 degrees Fahrenheit temperature continued for 48 hours, proper treatment becomes mandatory.
What are the treatments for diarrhea?
Adults should replenish the loss of water by having sufficient water and other low-sugar, non-caffeinated and low-fat beverages while avoiding milk. Eating fatty or greasy food is a strict no-no; following the Diarrhea diet or BRAT diet without alcohol and spicy food can help. In case one is experiencing nausea, sucking ice chip can be a good option. Also, avoid exercising during the treatment course to keep away dehydration. Other medical and preventive measures include:
- In case the Diarrhea is caused by a virus, antibiotics will not be effective. However, in other cases, antibiotics will help in alleviating the symptoms and shorten its duration. In case of Traveler’s Diarrhea, antibiotics are most useful.
- In certain medicines are triggering diarrhea, it will be better to change the medication by consulting with a doctor.
- Drink fluids and consume foods rich in fiber, iodine, and potassium like skinless potato, bananas, fruit juices, soups, chicken broths, salted crackers, and oatmeal.
- Avoide lactose, fructose, caffeine, sugar-free candies, gums, etc.
- In some cases, intake of probiotics is helpful in treating Diarrhea associated with antibiotics.