A Brief Insight Into The Symptoms Causes And Treatment Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis or DVT is a condition of the veins in the lower part of the body, where a blood clot is formed inside the veins, interrupting the natural blood flow. Specially occurring in the lower legs or the thighs, DVT commonly affects people who are aged above 50 years. Keep reading to know more about its symptoms, causes, and available treatment solutions.
Symptoms
Majority of the patients suffering from deep vein thrombosis, exhibit no symptoms at all.
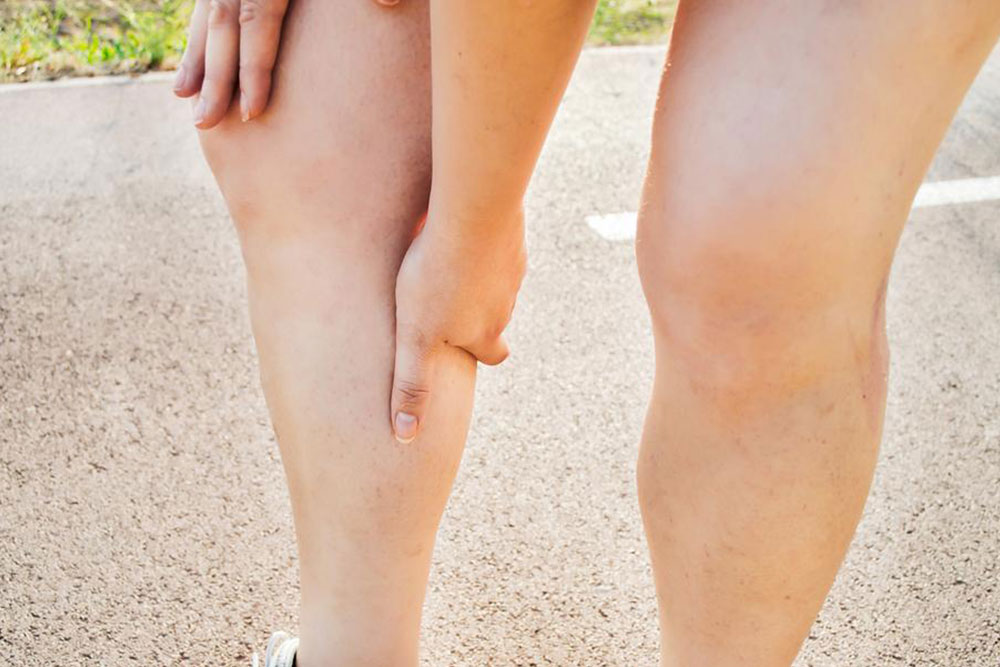
- Unbearable pain in the legs
- Tenderness or pain in the legs, especially when walking or standing
- Swelling in both or any one leg
- Discoloring or redness of the skin of the affected leg
Causes
The blood clots in the veins of the lower part of the body can be formed due to a number of reasons. Anything that prevents the blood from flowing normally interferes with its normal circulations and causes it to clot. This includes surgery, injury, and intake of certain medications, certain health conditions, as well as being overweight. Such condition may result in causing DVT.
Treatment
- Medications: There are a number of medications available for the treatment of DVT. The doctor may prescribe you a single or combination of medications that can prevent the risk of clotting of blood, depending on the condition of the patient.
- Filters: For those who aren’t able to take blood thinners, filters are put inside the vena cava, the large vein in the abdomen, for preventing the blood clots formed in the legs.
- Compression stockings: Compression stockings are known for lowering the chance of clot development as well as preventing swelling. As it also reduces the recurrence of DVT, the doctor may suggest the patient wear these on a regular basis.
It is suggested to opt for immediate medical treatment if one is suffering from deep vein thrombosis. If one ignores the condition for a long period of time, then it can lead to a more serious consequence where the blood clots may become loose and lodge in the lungs, causing the health condition to deteriorate further, resulting in chest pain, shortness of breath, and severe lightheadedness along with sudden coughs containing blood.